Botox for Overactive Bladder
What is Botox?
Botox® is a prescription medication that is injected into the bladder muscle and is approved to treat overactive bladder symptoms in adults 18 years and older after they have failed behavioral modifications and medication(s).
How Does Botox Treatment Work?
Botox treatment works by calming the nerves that trigger the overactive bladder. In your body, chemicals travel from nerve cells to muscle cells to make your bladder contract so that you can urinate. With OAB, these muscles contract uncontrollably.
Botox is injected into the bladder muscle and works on the nerve to help block the signals that trigger OAB.
Botox is not a daily treatment. Its duration may last 3 to 12 months for patients based on indication and dosage used. For most patients with OAB Botox typically lasts about 6 months.
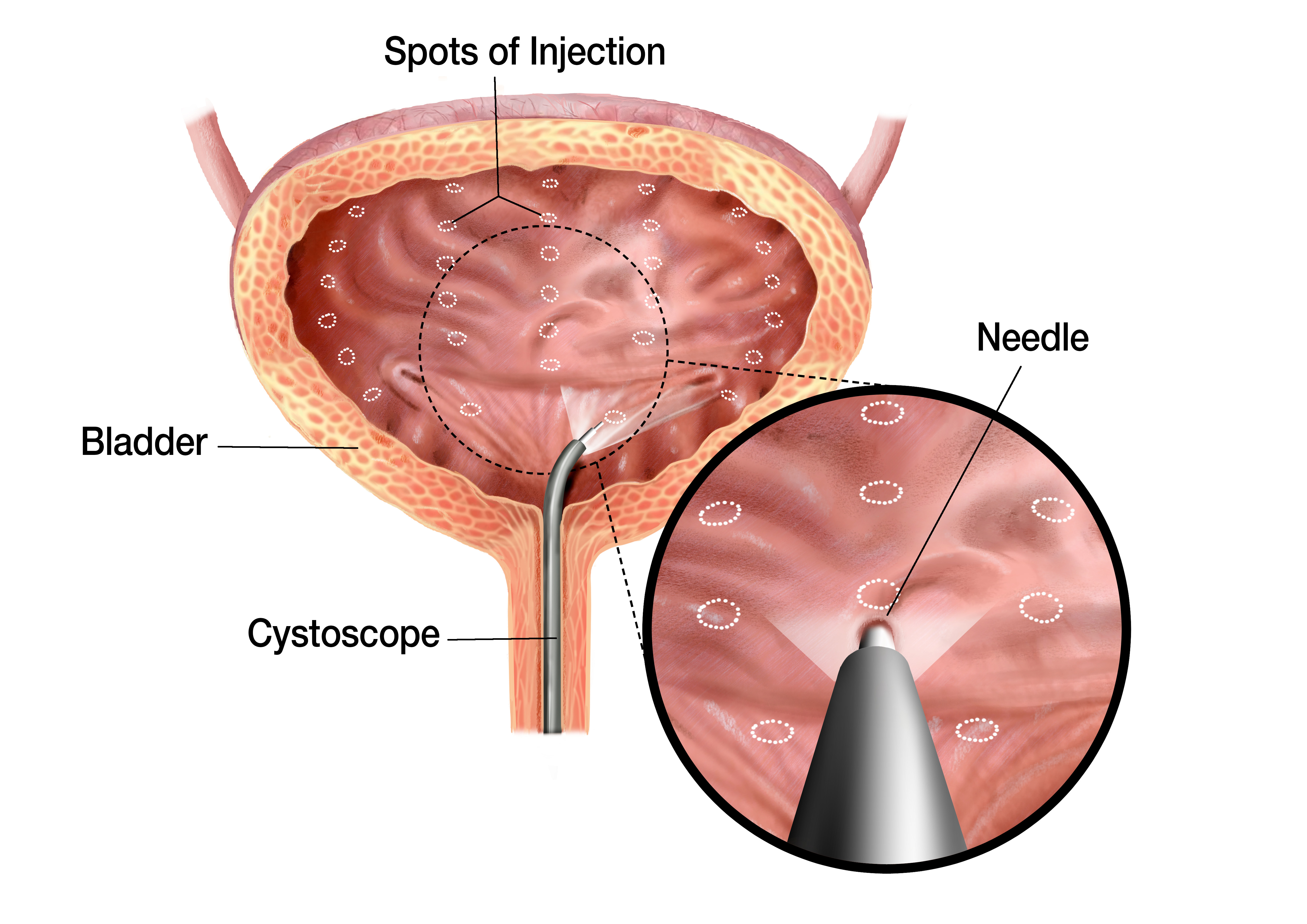
How is Botox Inserted Into the Bladder?
- The Botox procedure is typically performed in your provider’s office or an Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC).
- Your bladder will be filled with a numbing solution such as lidocaine to help ensure your comfort during the injection of Botox. This numbing solution will sit in your bladder for approximately 15-30 minutes.
- Once your bladder is numb, your provider will gently place a cystoscope through the urethra and into your bladder.
- Botox is delivered through the cystoscope. Several quick injections are delivered into the bladder muscle.
What are the Side Effects of Botox Treatment?
While not common, side effects from Botox therapy can include:
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Inability to fully empty your bladder
